Introduction
Architecture
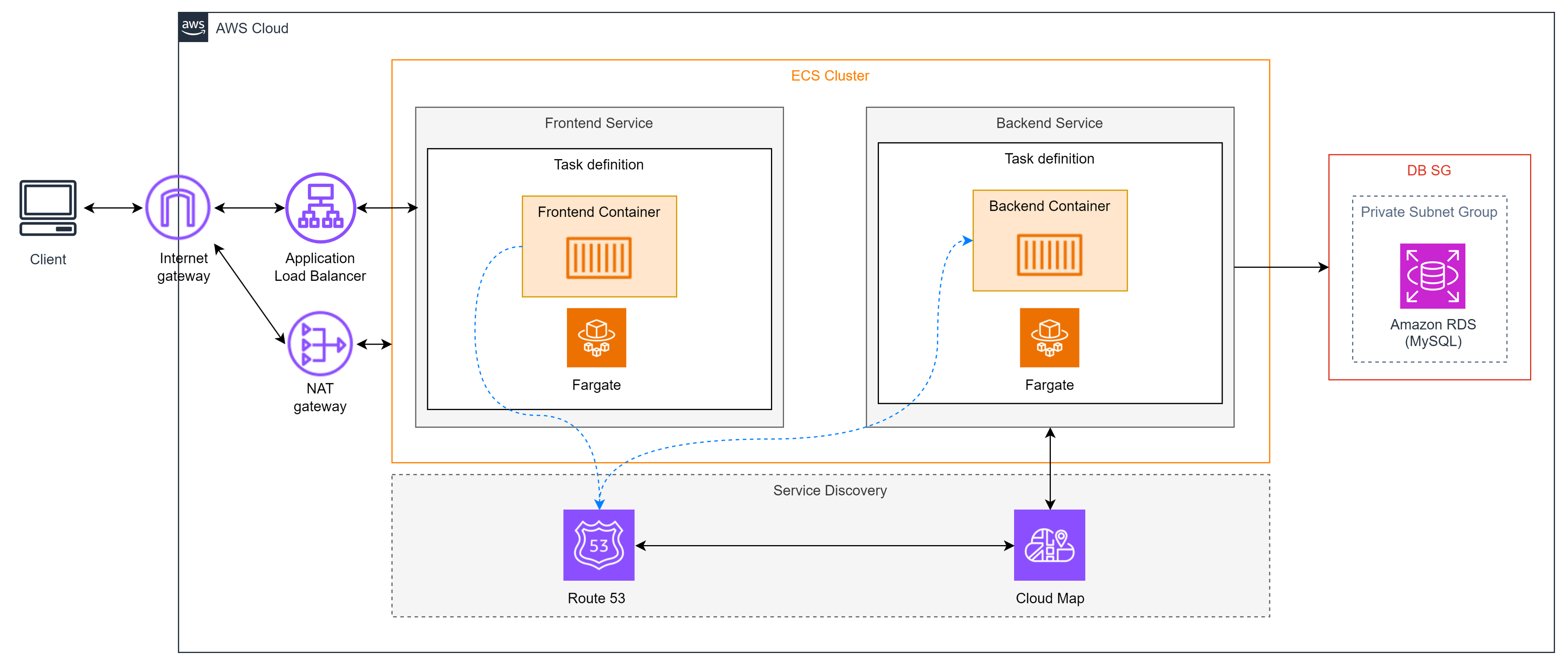
Amazon Elastic Container Service (ECS)
Amazon Elastic Container Service (Amazon ECS), as defined by AWS, is a highly scalable container management service that makes it easy to run, stop, or manage Docker containers within a cluster. You can host a serverless infrastructure by running services or tasks using the Fargate launch type, or use the EC2 launch type to run EC2 instances. Amazon ECS is often compared to Kubernetes, Docker Swarm, and Azure Container Instances.
Amazon ECS runs containers in a cluster composed of multiple Amazon EC2 instances with Docker pre-installed. This service handles container installation, scaling, monitoring, and managing these instances (launch/stop) through both APIs and the AWS Management Console.
Amazon ECS simplifies the view of EC2 instances into a pool of resources, such as CPU and memory.
You can use Amazon ECS to deploy containers through clusters, depending on the resources you need, independent policies, or flexibility. With Amazon ECS, you don’t need to operate your own configuration and cluster management system or worry about scaling your infrastructure management.
Amazon ECS is a regional service that simplifies running container applications across multiple Availability Zones (AZs) in the same region. You can create an ECS cluster inside a new or existing Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). Once a cluster is created and running, you can define tasks and services, specifying which Docker container images will run through the clusters.
Amazon ECS Task definitions
In Amazon ECS, Task definitions are created to define pre-launch configuration settings for Docker containers in Amazon ECS. The configurations that can be defined in a task definition include:
- Docker image to use.
- The amount of CPU and memory used in the task or each container within the task.
- Launch type (specifying the infrastructure to run).
- Networking mode for the containers.
- Log configuration for the task.
- How to handle task execution.
- Commands to run when the task starts.
- Volume definitions.
- IAM roles used to run the task.
Amazon ECS Services
In Amazon ECS, Service is a configuration that allows one or more tasks to be run continuously in a cluster and automatically maintained. Tasks and services can be run on serverless infrastructure managed by AWS Fargate or on user-managed infrastructure such as EC2 clusters.
Amazon ECS Cluster
An Amazon ECS Cluster is a resource management unit used to deploy containers in AWS ECS. When you fully define task definitions and services for an ECS Cluster, the cluster creates the necessary resources to deploy containers. An ECS cluster is a group (or a single) of virtual machines hosting containers.
Cluster Scaling và Service Scaling
In ECS, a Cluster is a group of resources (EC2 instances or Fargate) used to run containers. Cluster Scaling is the process of increasing or decreasing the number of resources in the cluster based on workload demands. This can be done manually or automatically using Auto Scaling. With Auto Scaling, the cluster automatically adds or removes instances based on task count, CPU usage, or RAM, optimizing resources.
Service Scaling in ECS refers to adjusting the number of tasks (containers) a service is running. ECS supports Auto Scaling for services based on specific rules, such as CPU or memory usage, request count, or other metrics collected by Amazon CloudWatch.
Rolling và Blue/Green Deployment
Rolling Deployment is a method for gradually updating the containers of a service, meaning that new versions of the container are rolled out slowly to replace the old versions. ECS will stop running the old containers and gradually create new ones, ensuring enough resources are available and that the service is not interrupted. Rolling deployment is a safe deployment strategy, minimizing downtime, but it may take more time if many containers are involved.
Blue/Green Deployment is another deployment strategy in ECS that reduces risks when updating software. In this method:
- Blue is the current version of the running application.
- Green is the new version of the application, deployed in parallel with Blue. Once Green is ready and successfully tested, traffic is shifted from Blue to Green via a Load Balancer. If any issues arise with Green, traffic can be reverted back to Blue without downtime. AWS CodeDeploy and Application Load Balancer are commonly used to support Blue/Green deployment strategies.